July 11, 2024
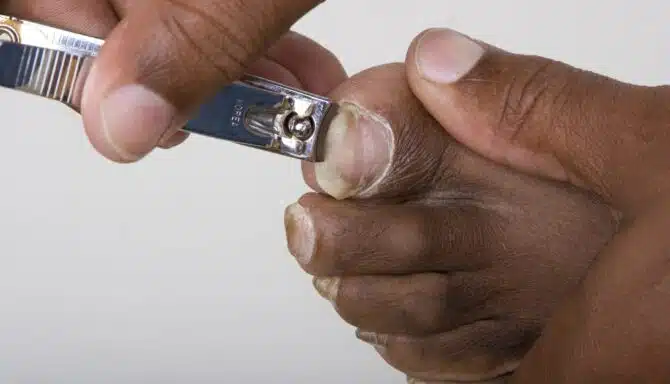
There's always the right tool for the job. Using each tool for its intended purpose is best, or you risk doing more damage than good. That's why fingernail clippers and toenail clippers exist.
To understand why, it's important to understand the difference between toenails and fingernails. Toenails are thicker, harder, and grow slower than fingernails because your feet and hands serve different functions. Toenails also have a greater surface area.
In this blog post, we explain why you should avoid using fingernail clippers for your toenails and opt for toenail clippers exclusively.
Reduce the risk of bacterial or fungal contamination
For one, separating your nail tools prevents contamination and possible spread of bacteria and fungus. Given how exposed your hands are every day, you wouldn't want to spread any bacteria to your feet.
When in doubt, clean your clippers with 70%—90% isopropyl alcohol.
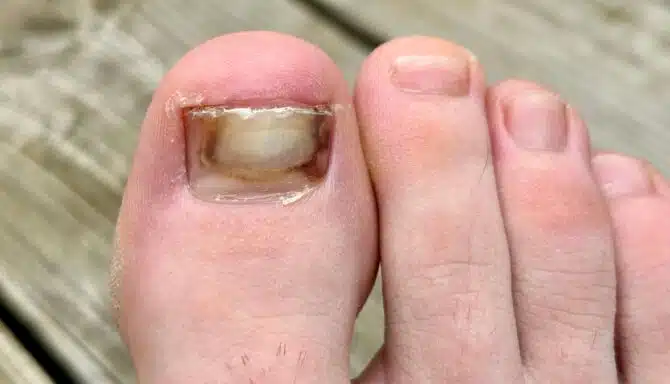
Fingernail clippers may not work on toenails
When looking at fingernail vs. toenail clippers, the size difference is stark. Fingernail clippers are smaller, narrower, and curved. Toenail clippers are larger, wider, and straight across, as you should trim your toenails straight across. Cutting them with a curved edge increases your risk of ingrown toenails.
If you want more guidance on choosing the tool for your toenails, read our blog post on our top choices for toenail clippers.
Limit the risk of cracking and damaging your toenails
Using sharp, rigid toenail clippers makes trimming easy and more effective. Using fingernail clippers means you'll need to apply more pressure to cut the nail and risk damaging or even cracking the toenail.
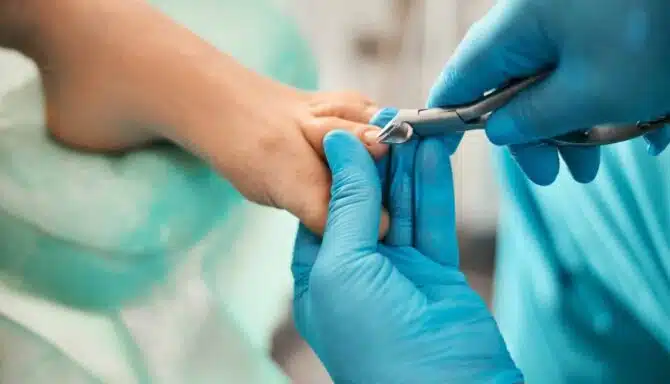
If you don’t have the right tools, enough time, or simply the confidence to focus on a nail trim, try a medical pedicure instead. It includes the right nail trimming procedure and includes moisturization, thorough cleaning, and more. Before the nail trim, a chiropodist also examines your feet for other foot conditions.
Prevent ingrown toenails
You'll also notice the curvature of fingernail vs. toenail clippers. Fingernail clippers are curved and meant to follow the contours of your fingernails. On the other hand, toenails are plateaued and should be cut straight across. Using a curved tool on your toenails puts you at risk of jagged edges, nail splitting, or could be a root cause of ingrown toenails.
If you wish, use a nail file to round the edges. This tool is necessary for properly smoothing the edges of the nails. After the trimming, there will likely be some jagged edges, sharp corners, and “spikes.”
July 4, 2024
A toenail falling off can be uncomfortable and cause concern about damage to the toenail. The goal is to preserve the toenail's state to prevent further damage.
Fortunately, if you take a few proactive steps, you can reduce the discomfort and promote healing. Here are our six tips for managing a toenail on the verge of falling off.
1. Keep the toenail area clean and dry
Wash the toenail gently and often. We recommend using mild soap and water to keep it clean. Next, pat dry so as not to snag the toenail with a towel.
2. Cut the nail carefully and slowly
Use clean, sterilized nail clippers to remove any dangling or loose portions of the toenail. Cut straight across without digging into the surrounding skin. The goal here is to prevent further snagging or tearing down the road. Improperly cutting your nail may also increase your risk of an ingrown toenail.
In addition to trimming the toenail straight across, you should trim the toenail slowly. Don't over-cut it. Be patient with toenail growth. (It may take months to a year for a nail to fully grow out.) If in doubt, let our toenail specialists in Toronto trim your toenails for you as part of a medical pedicure.
3. Use a non-stick bandage to protect the area
We recommend applying a bandage or non-sticky wrap to your toe. (Adhesive can attach itself to the toenail and be difficult to peel off without grabbing onto it.) A protective layer keeps an otherwise exposed nail bed safe. Replace the bandage regularly and keep the area dry to promote healing.
4. Antiseptic ointment is your friend
Use an antiseptic ointment or petroleum jelly on the exposed nail bed to keep it moisturized and prevent infection. This may help soothe any discomfort from the loose toenail.
5. Choose comfortable and roomier footwear
You'll want to reduce pressure as much as possible to prevent a loose toenail from falling off. Given that we wear footwear so often, finding shoes with ample fit can help prevent further damage to the toenails.
6. Avoid intense activity
Reduce your activity level if it puts excessive pressure or strain on the affected toenail. For instance, running or high-impact sports like soccer could increase the risk of the toenail getting snagged or torn off. Give your toe some rest, and return to physical activity gradually.
June 20, 2024
At first glance, our toenails look like a single nail, and that's about it. However, beneath the surface is a more complex structure that makes up the nail and the bed below it. This is our toenail anatomy.
Toenails and fingernails are made of Keratin. Keratin is a type of protein that gives the nail strength and protection. (There are many types of Keratin. It also comprises hair and your epidermis.) Toenails differ from fingernails in a few ways, namely their thickness and growth rate, as the external forces on your toenails are greater than those on your hands.
Today, we explore toenail anatomy and how each component affects foot health.
Layers of the toenail
Nail plate
The nail plate is the easiest part of the toenail anatomy to recognize. It's the nail itself. The colour and texture of the nail plate can vary based on factors like health, genetics, and lifestyle habits.
Nail bed
Next, we go a bit deeper. The nail bed is beneath the nail plate. Just like sheets and blankets are the nail plate, imagine the nail bed is the mattress or bed frame below. The nail bed is a layer of skin that nourishes the nail as it contains blood vessels and nerves. It is also the growth engine behind the nail plate.
If you damage the nail bed, you'll notice nail plate abnormalities or reduced growth rates. Sometimes, a damaged nail bed will cause you to lose a toenail or experience a discoloured toenail. A subungual hematoma occurs within the nail bed and can cause a black toenail.
Lunula
The lunula, or "half-moon," is the pale, crescent-shaped area visible at the base of the nail. It represents the edge of the nail matrix, where new nail cells are generated. Eventually, nail growth from the lunula extends out to the outer edges of the nail, at which point you'd trim them.
Nail matrix
The nail matrix is the tissue beneath the cuticle at the base of the nail. It produces new nail cells, pushing older cells forward and resulting in nail growth. Damage to the nail matrix can affect the quality and growth rate of the toenail. Each nail matrix produces 196 layers of cells that combine to make your toenails.
June 6, 2024
Our feet and toes change in various ways as we age. One of these changes is toenail thickening.
For some of us, toenail thickening can be more than just a minor inconvenience. It can make it difficult to cut and maintain our toenails, and can even cause pain and discomfort. In this article, we'll explain the causes of thickened toenails, and some possible treatments.
Why Do Toenails Thicken with Age?
Nails are made from a protein called keratin, which is produced at the nail plate at the base of the nail. Nail growth happens when nail cells multiply within the base of the nail and are pushed forward. However, as we age, the growth rate slows down, so the nail cells just pile up on top of each other, which causes them to get increasingly thicker.
Toenail thickening is often a result of several factors:
Reduced blood circulation
The most common cause of toenail thickening is decreased blood circulation to our feet. This diminished circulation means fewer nutrients and oxygen reach the toenails, causing them to thicken over time. Age is one of the risk factor for reduced blood circulation to the feet.
Natural wear and tear
Years of use can damage our toenails. Factors such as ill-fitting shoes, repetitive stress from activities like running or walking, and even minor trauma can contribute to thickening. Essentially, when our toenails experience trauma, they thicken to protect themselves. As we age, wear and tear on our toenails can accumulate, which can cause them to thicken.
Fungal infections
Older individuals are more prone to fungal infections of the toenails, which can cause thickening, discoloration, and brittleness. These infections often thrive in warm, moist environments like sweaty shoes or communal areas.
Underlying health conditions
Medical conditions like psoriasis, diabetes, and peripheral arterial disease can also influence toenail health. These conditions affect circulation, which in turn slows toenail growth and causes toenails to thicken.
Tips for toenail care as you age
As you age, proactive steps can be taken to maintain healthy toenails and minimize thickening. By following these tips, you can feel more in control of your foot health and well-being.
Regular trimming
Toenail thickening can make trimming and maintaining your toenails extremely difficult. Fortunately, a licensed chiropodist is trained to specifically deal with this. A licensed chiropodist can ensure your toenails are trimmed properly to prevent ingrown toenails, promote healthy toenail growth and reduce thickening. A licensed chiropodist can also use special tools over the toenail to thin it out, which will make the toenail easier to cut and maintain. Best of all, this is all done in a sterilized environment, so you don't need to worry about fungal infections (did you know 52% of people get fungal infections after visiting nail salons?) If you decide to trim your toenails at home, make sure you invest in quality toenail clippers and avoid cutting them too short.
Proper foot hygiene
Wash your feet daily with soap and water, ensuring they dry thoroughly, especially between the toes. Also, wear flip flops in public spaces to avoid contracting fungal infections.
Comfortable footwear
Choose shoes that fit well and provide adequate support. Avoid narrow or tight shoes that can put pressure the toenails and contribute to thickening.
Moisturize regularly
Apply moisturizer to your feet to keep the skin and nails hydrated. This can prevent cracking and thickening of the toenails, especially in dry climates.
Foot protection
Wear protective footwear in risky environments like communal areas or outdoors. This can help prevent injury and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Manage underlying conditions
If you have underlying health issues like diabetes, it's important to remember that they can be effectively managed. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can improve foot circulation and reduce the risk of complications like toenail thickening.
May 30, 2024
As summer approaches, our feet emerge from the confines of socks and boots, ready to step into sandals and flip-flops. However, after months of neglect and hiding, our feet may not be in the best condition to be on display. This is where medical pedicures come in—a treatment that goes beyond mere aesthetics. Let's delve into the benefits of medical pedicures and why they should be on everyone's summer to-do list.
Professional attention to foot health
Unlike traditional pedicures, medical pedicures are performed by trained professionals called chiropodists. They prioritize foot health, ensuring your feet are healthy and feel good. Chiropodists are equipped to address various foot conditions such as calluses, corns, ingrown toenails, and fungal infections. They can also notice and diagnose other things that may be cause for concern, like poor circulation, warts, flat feet, and other foot conditions that may be affecting you. Most importantly, chiropodists can provide professional tips and advice on foot care.
Preventative foot and nail care
Regular medical pedicures can help prevent many standard foot problems before they even start. Addressing issues like calluses and ingrown toenails early on can avoid more severe complications. In addition, toenails grow faster in warm weather, so a medical pedicure in the summer is timely.
Customized treatment
Medical pedicures are tailored to your specific foot needs. Whether you have dry, cracked heels, thickened toenails, or sensitive skin, the treatment can be adjusted to address your concerns effectively. Chiropodists will assess your feet and recommend the appropriate action, ensuring you receive personalized care at every step.
Hygiene and safety
One of the primary benefits of medical pedicures is the emphasis on hygiene and safety. Sterilized instruments, disposable blades and discs, and stringent cleanliness protocols are standard practice in foot clinics. All cleaning protocols are regulated by Health Canada and the College of Chiropodists of Ontario. This reduces the risk of infection and ensures a safe, worry-free experience, especially those with compromised immune systems or diabetes.
Stress relief
It's worth remembering the relaxing aspect of a medical pedicure. Beyond the therapeutic benefits for your feet, the experience can be incredibly soothing for your mind and body. Taking time out of your busy schedule to pamper yourself can lower stress levels, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being.
May 13, 2024
Summer foot care and pedicures - can you name a more iconic duo? Showing off a sleek pedi is one of the best ways to enjoy the warm months. But safe pedicures differ greatly from your run-of-the-mill cosmetic pedicure, so it’s important to be on the lookout for the safest way of avoiding pedicure infections. We’ve got 3 pedicure safety tips you should follow before you hit the salon!
Top 3 Pedicure Safety Tips
Choose clean salons or foot clinics
Avoid certain tools
Practice aftercare
Choose Clean Salons or Foot Clinics
Only visit nail salons that demonstrate good practices. Be on the lookout for:
An organized workspace.
Equipment sanitization protocols. An autoclave with steam sterilization is best.
Employees visibly maintaining hygienic standards.
Employees using disposable liners in the foot baths, and cleaning and filtering them between uses.
Fresh linens (if applicable).
Clean floors and surfaces.
Clean uniforms on employees.
Clear labels on products.
Clients wearing protective footwear when walking around.
Another good tip is visiting your nail salon when they first open in the morning, when everything is cleanest!
Pedicures at Feet First Clinic
Foot clinics are where you can get a medical pedicure, which tends to be safer than a cosmetic pedicure.
Appointments don’t happen in communal areas, unlike salons, so you’re already in a safer environment with less people spreading contagious fungal infections. And although you’ll be skipping the polish (you can always apply it yourself afterwards!) and foot bath (again, you can do this at home - foot baths at nail salons are not hygienic, especially if the bath has jets), you’ll be enjoying so much more than you can get from many salons. This includes:
Guaranteed use of sterilized, safe tools.
A thorough cleaning of the entire foot with alcohol.
An inspection of your feet from a chiropodist who can recognize foot conditions.
Thorough cleaning of dead skin(onychophosis) under the nails.
Callus softening or removal.
Learn more about what happens during a medical pedicure and the differences between a cosmetic vs. a medical pedicure.
Avoid Certain Tools
Nail technicians in salons use many tools, but you should kindly request they skip some of them. One of these is the foot rasp or “grater” they use to scrape the bottom of the feet. It can be overly abrasive and damage the skin, leading to irritation and cuts. Strong skin is a barrier for contaminants, and damaged skin welcomes dirt and infections.
To protect your feet even more, you can skip tools that don’t appear to be properly sanitized or cleaned between uses, or avoid tools with visible signs of wear and tear.
Practice Aftercare
After getting your pedicure, it’s up to you to keep on top of proper foot care! Here’s what to do:
Avoid tight shoes that crowd the toes. This can cause ingrown toenails.
Wash your feet every day with gentle soap before thoroughly drying.
If you must cut your own toenails, only trim straight across, avoiding shaping.
Moisturize and exfoliate your feet.
Wear clean cotton socks and change them frequently.