July 22, 2024
Sometimes with aging feet comes the development of toe deformities, particularly hammertoes. Studies show that approximately half of women over 70 have some version of a toe deformity (but they can happen to anyone). Many assume correcting hammertoes always leads to a daunting surgery, but guess what? Surgery is not usually the first option and is generally only considered when the toe becomes rigid, or other complications arise. Read today’s article to discover the best non-surgical solutions for hammertoes and toe alignment techniques that achieve amazing results.
Top Hammertoe Treatment Options
Innovation in foot care and toe straightening methods have lead to plenty of non-surgical solutions for hammertoes and the pain they cause, including:
Splinting, taping and bracing
Custom orthotics and new footwear
Shockwave therapy
At-home exercises
Other treatments
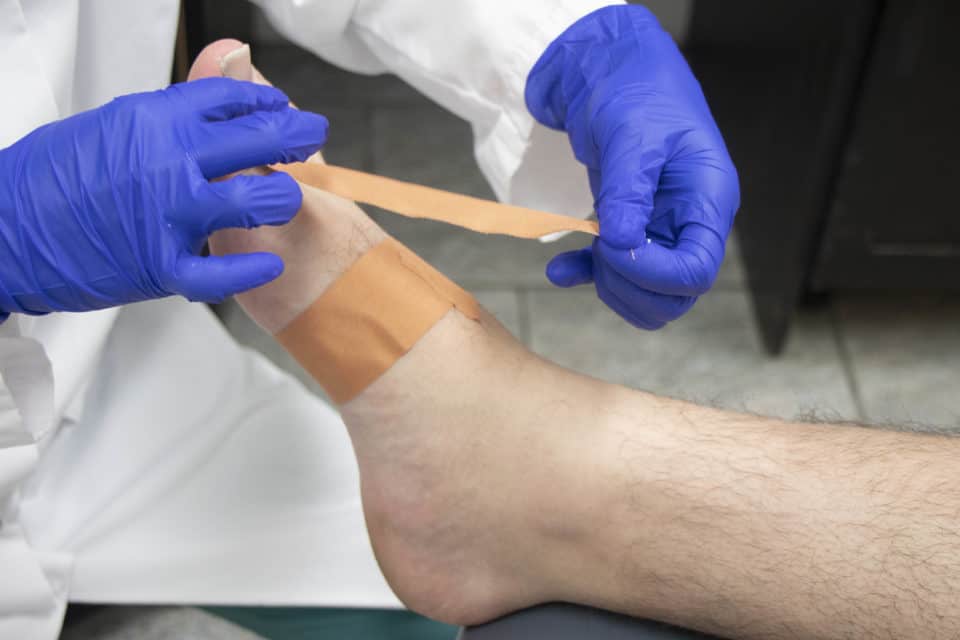
Splinting, Taping and Bracing
These non-invasive tools are great for dealing with toe curvature. All performed by a licensed Toronto chiropodist, splinting, taping and bracing helps straighten the toe, reduces friction and discomfort (corn development is common for people with hammertoes) and provides support and alignment.
Custom Orthotics And Footwear Changes
Custom orthotics are all about placing each part of your foot where it’s supposed to be, including toes. Wearing orthotics can properly align the joint in your toe and relax the burden on the affected tendons. Most importantly, they'll offset and redistribute pressure away from the toes. This will reduce strain on the hammertoes when you walk, which will help prevent them from getting worse.
As for footwear, avoid high heels if you have any toe deformity; they’re notorious for making hammertoes worse. Wear wide shoes, maybe even orthopedic shoes, that allow your toe abnormalities to exist comfortably and reduce pain as much as possible. Most importantly, make sure your shoes fit: If your shoes are too short, your toes will curl, which will make your hammertoes worse. (In fact, ill-fitting footwear is a major contributing factor to hammertoes.)
Shockwave Therapy
It’s clear that when you have hammertoes, your joints and tendons take a hit. They stiffen up, become quite painful, and may even weaken your muscles over time. Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that may help treat your tendons and ligaments.
At-Home Exercises
Check out exercises and stretches that help treat the top of the foot to soothe your hammertoes and strengthen your feet and muscles in general. Many of these target the toes and surrounding area. Strengthening the muscles in your feet ensures that the toes and joints don't get overworked or strained when you walk, which helps manage hammertoes and provides hammertoe pain relief.
Over-the-Counter Products
Gel separators, toe spacers, pads, cushions and more can help you take control of your hammertoes without resorting to surgery. Call your local Toronto foot clinic to see what they have in stock!
October 21, 2023
Runner's knee is a condition that causes pain around the front of the knee, particularly near the kneecap. Don't let the name fool you: runner's knee doesn't just affect runners. Individuals who engage in repetitive knee-bending activities, such as cycling, jumping, or squatting, can experience this form of knee pain. The condition is characterized by discomfort or pain often felt during and after physical activities.
Whether you're a seasoned marathoner or lacing up your running shoes for the first time, understanding the ins and outs of this common ailment is helpful for preventing and managing its onset.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into runner's knee – its causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and rehabilitation techniques – to ensure that you stay pain-free and on your feet.
Runner's knee: What is it?
Runner's knee, formally known as patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS), is a condition characterized by pain around the front of the knee. Any activity that repeatedly stresses the knee cap or the areas around the knee cap can aggravate the condition. It is more common in women than men. This is believed to be due to a greater susceptibility to knee misalignment in women.
Runner's knee symptoms include:
Pain around the knee cap, especially during activities that involve bending the knee, such as running, walking downstairs, or squatting.
Pain after prolonged sitting and a stiff feeling in your knee
Cracking or popping sensation
Swelling and inflammation in and around the patella
What cause's runner's knee?
Many causes of runner's knee are not specific to the knee, but rather are abnormalities with the surrounding muscles and joints. Because the knee is a hinge joint, it relies on many different parts of the leg to properly perform its job.
Common causes of runner's knee are:
Misalignment of the patella: Improper tracking of the patella can lead to increased pressure on the joint.
Muscle imbalances: Quad, hip, and knee imbalances can lead to biomechanical deficiencies that overexert the knee.
Overuse: Repeated knee bending and straightening during activities can cause excessive stress on the patellofemoral joint, leading to irritation and pain.
Poor biomechanics: Issues with how the lower extremities function during movement, such as flat feet or overpronation, can contribute to developing a runner's knee.
Inadequate warm-up or stretching: Failing to properly warm up before exercise, or neglecting to stretch, can increase the risk of developing PFPS.
Too much, too soon: A sudden increase in activity level, such as increasing mileage or intensity too quickly, can strain the knee joint and lead to a runner's knee.
Inadequate footwear: Improper footwear that does not provide adequate cushioning and support can contribute to knee pain.
How do I treat runner's knee?
There are several ways of treating a runner's knee. First and foremost, understanding the cause(s) will help you get back to being healthier faster. Common treatments include:
Rest and ice: Give your knees time to rest, and apply ice to reduce inflammation and pain.
Reduce intensity: Reduce or stop the physical activity that could be causing the pain. Alternatively, reduce all activity while you consult a professional to diagnose the exact cause, at which point you can slowly re-introduce physical activity. You can also try low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling to maintain fitness while giving your knees a break.
Physical therapy: Physiotherapy, massage therapy, and a strength program can help strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve biomechanics. Engage in exercises stretching and strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, hip, and calf muscles.
Orthotics and proper footwear: Custom orthotic inserts or appropriate footwear can help correct biomechanical issues contributing to the condition. A shoe fitting and video gait analysis can help reveal any biomechanical deficiencies and provide a helpful guide into choosing the right shoe.
Patellar taping: Taping techniques can help reposition the patella and reduce pain during activity.
When to see a chiropodist for a runner's knee?
If the pain persists despite conservative treatments, consult a healthcare professional like a chiropodist for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Addressing the runner's knee early is essential to prevent further complications and ensure a timely recovery.
September 14, 2023
Bunions - or for those who have them, the painful, bony nuisances that form at the big toe joint - are a common foot condition for older people, especially women. While surgical intervention can sometimes help those with debilitating bunions, lifestyle changes and effective management strategies can help you avoid a bunionectomy in many cases.
Moreover, surgeries are usually only necessary if your bunions cause regular functional and mobility problems and chronic pain, which is often not the case.
Let’s look at the causes and symptoms of bunions and explore how you can manage them without invasive measures.
Image Credit: Fabrikasimf from Freepik
Symptoms of Bunions
Bunions protrude from the side of your big toe, forming an “L” shape angle. Additional symptoms of bunions include:
More corns and calluses than you would normally have due to the big toe rubbing against the second toe
Mild redness, pain, and swelling
Limited movement in the big toe
Severe bunions can cause overlapping toes, pain that doesn’t subside, and toe angulation of more than 40 degrees.
Photo credit: istock
Causes of Bunions
The main culprit? The wrong shoes!
Wearing high heels may make you feel good about yourself aesthetically, but they can damage your physical health over time and are one of the main causes of bunions in women. Narrow, tight, and pointed shoes (often the design of stilettos and other types of heels) squeeze and push your toes together and forward unnaturally, increasing pressure on the big toe and leading to bunion formation.
Having another condition that targets the joints, like osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid arthritis, or one that causes an abnormal gait, like flat feet, can also hint at bunions in your future. Activities where your toes are more vulnerable than the rest of your feet, like dancing, may also be a risk factor.
Image by rawpixel.com from FreePik
Bunions: Management Strategies
You can tackle a mild bunion problem from home and with regular visits to the chiropodist. Here are some of the best ways you can prevent bunions from ruining your day or getting worse:
Change your footwear: Ditch the high heels for comfortable alternatives and shoes with extra room in the toe box. If you’re not sure where to start, attend a shoe fitting.
Try bunion splints or aligners. They can hold the affected joint in place.
Therapeutic taping can help hold the joint in place and temporarily relieve pain.
Shoe stretching may help secure more room in the toe box and take pressure off the bunion.
Try these 5 simple exercises for bunions. They are relatively easy, low-impact, and don’t require exercise equipment.
Get custom orthotics. Orthotics might reduce excess pressure on the big toe joint and correct any biomechanical issues that are contributing to your bunions (plus they're also super comfortable!).
Ask about shockwave therapy. This innovative, non-invasive, and quick procedure is an effective management strategy for bone and joint conditions. It can help relieve pain caused by muscle tightness around the bunion.
It's important to remember that bunions don't disappear like other conditions sometimes do. But successfully practicing these treatment methods can help you avoid surgery.
If you suspect your bunions are too severe for these strategies, speak to your family doctor.
Bunion products available at Feet First Clinic
April 20, 2023
Since women are more likely to experience foot pain and conditions, a significant focus of women's health should always be foot health. According to Foot Health Facts, narrow footwear that cramps the forefoot and squeezes the toes is the primary reason women are prime targets for foot health issues. Furthermore, common foot problems in women can arise after years of wearing shoes with little arch support and unstable heels. Today's article will discuss the most common foot problems women struggle with and prevention and treatment options.
Common Foot Problems in Women
Bunions
Plantar fasciitis
Arthritis
Hammertoes
Plantar Fasciitis
Medical News Today notes women risk developing plantar fasciitis more than men. This may be due to post-pregnancy foot changes and the effects of wearing unsupportive footwear for years; both can lead to plantar fascia strain and subsequent stabbing heel pain. The best way for women to prevent and treat this painful condition is to only wear high heels on special occasions and choose comfortable heels with cushioning and a stable heel. For daily activities, opt for shoes with sufficient arch and heel support (most important) and thick soles and cushioning. But it's also important to find shoes with that create a healthy environment for your feet (i.e.: enough room in the toe box, breathability, etc.) to prevent other conditions.
Maintaining a healthy weight can also prevent too much pressure on the plantar fascia. To help, women can stretch their feet and perform daily exercises that work the plantar fascia and calf muscles (see an example below!). And lastly, orthotics with arch support can distribute the pressure on your feet more evenly.
https://www.pinterest.ca/pin/782007922800908317/
Bunions
Again, low-quality shoes are the main culprit behind women developing bunions, but genetics may also play a role. Bunions may also be at their worst during menopause or pregnancy.
Some women may require intervention from a surgeon to eliminate severe bunions. But many can try non-invasive methods like bunion pads, inserts and orthotics, and frequent rest periods with compression and ice packs. The most worthwhile preventative measure is changing your shoes and giving your feet the support and room they deserve. Ensure all shoes have enough room in the toe box (cramped toes are a major risk factor for bunions) and are not too narrow.
Arthritis
Research suggests post-menopausal women suffer more from osteoarthritis than men because of estrogen fluctuations. There may be a connection between pre-menopausal estrogen levels and joint and cartilage health.
Targeted exercises are one of the best ways to prevent and treat most types of arthritis (not just osteoarthritis!). Moreover, Feet First Clinic's beginner's guide to exercises for arthritis Part 1 and Part 2 outline beneficial exercises, the steps involved and why they're so useful. These routines also consider that arthritis can be very limiting and ensures all movements are manageable. Other forms of treatment include braces or canes (in severe cases), anti-inflammatory pain relievers, orthotics that support the ankle and the foot (also good for prevention), physiotherapy and orthopedic footwear.
Hammertoes
Like bunions, hammertoes affect women because they are more likely to wear excessively tight and unsupportive shoes, causing the toes' middle joints to bend more and more over time.
To avoid and manage pre-existing hammertoes, ensure your shoes have at least half an inch of room between the toes and the end of the shoe. Additionally, women should avoid high heels on most days and only wear them if the heel is a "reasonable" height. It may also be wise to buy shoes with stretchy fabrics and avoid excessive fabric layers. They can force your toes into uncomfortable positions and make it difficult to accommodate pre-existing hammertoes. Inserts and pads can also be helpful for women by positioning the toes and feet more favourably. Furthermore, a chiropodist can use a splint or some tape to fix your toe in the proper, straight position.
Several medical devices can help with toe conditions
April 15, 2023
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common foot conditions out there, and it can also lead to another lesser-known condition --- heel spurs. Many foot conditions develop from poor lifestyle habits and neglecting proper footwear, foot hygiene, etc. That said, some conditions co-exist and present themselves after another condition is already present. This is the relationship that heel spurs have with plantar fasciitis; the former results from the latter.
This is good news in the sense that you can educate yourself on exactly what to do to prevent heel spur formation. This includes strengthening exercises and stretches you can perform at home to manage your plantar fasciitis. Additionally, you can benefit from a wide array of services from a Toronto foot specialist, including orthotic fittings and footwear recommendations. Feet First Clinic is here to give you some crucial info on heel spurs! If you have plantar fasciitis, you'll want to learn about how to prevent heel spur formation and how you can treat this condition if it does occur.
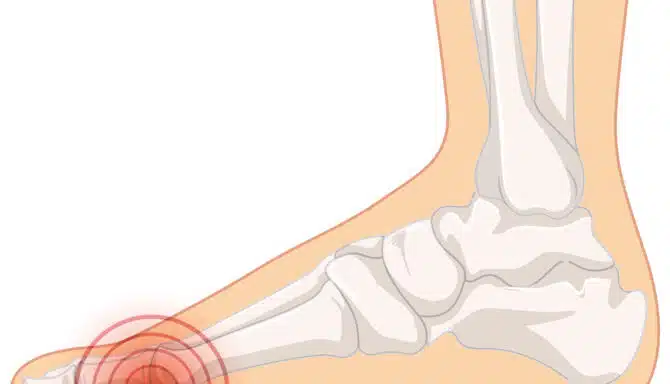
What is a Heel Spur?
A heel spur is a type of bone spur. More specifically, a spur is a smooth, bony growth made from calcium deposits that can take months to accumulate. According to Web MD, heel spurs form on the underside of the heel bone.
Commonly, heel spurs are a complication that can present in those who have plantar fasciitis. The latter is a condition that arises when the plantar fascia ligament becomes inflamed. This ligament connects your heel bone to your toes. People with spurs may notice heel pain, but it is usually a symptom of plantar fasciitis and generally not from the spur itself. That said, sometimes heel spurs do come with symptoms.
Heel Spur Symptoms
This plantar fasciitis complication is usually pain-free and asymptomatic. As a general rule, any noticeable heel pain is likely from plantar fasciitis and not from spurs. That said, in some cases, the following symptoms may be present as a result of heel spur formation:
Intermittent or chronic heel pain. It may begin as a "sharp jab" and progress into a dull ache. This pain may flare up after exercise that places pressure on the heel (walking, running, etc.).
Mobility problems.
Heel swelling.
Foot callus formation on the bottom of the heel. Your body is responding to the protrusion and attempting to provide extra protection and padding.
How Do Heel Spurs Develop?
If you're one of many people with plantar fasciitis, disregarding simple treatment methods for your inflamed plantar fascia can lead to heel spurs. Athletes with unchecked plantar fasciitis who spend time running and jumping are especially at risk; however, all plantar fasciitis patients are vulnerable.
Heel spurs develop when the ligaments and muscles in the feet experience consistent strain. You can also develop heel spurs after repeated vigorous activity eventually tears the membrane on the heel bone. As a general rule, heel spurs take months to build. This means you have plenty of time to manage your plantar fasciitis and avoid this foot condition.
I Have Plantar Fasciitis. How Can I Prevent Heel Spurs?
If you follow some simple treatment routines for plantar fasciitis, you can significantly reduce your chances of experiencing heel spurs. Not only that, but there are plenty of things you can do from home to manage plantar fasciitis. One of the best treatment options is routine foot stretches and strengthening exercises.
It's best to do these stretches and exercises at least twice per day, preferably before and after physical activity. Alternatively, you may notice your plantar fasciitis pain flares up in the mornings. If this sounds like you, you can do your first round of exercises when you wake up. These exercises and stretches help loosen your muscles and allow you to cope with heel pain. Below you will find some excellent exercises that help those with plantar fasciitis manage and control pain flare-ups. Click on the links for easy-to-follow demonstrations!
Plantar Fasciitis Exercises
Toe flex and raise
Towel stretch
Golf ball stretch
Rolling a tennis ball or frozen water bottle under the foot helps strengthen your muscles and soothes inflammation.
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Spurs: Other Treatment Options
In some cases, heel spurs may catch up with you before you can prevent them. If this sounds like you, don't worry. In the unlikely case that they come with symptoms, there are plenty of treatment options available. Most treatment options for heel spurs are the same methods used to treat plantar fasciitis. So, it's always wise to try and prevent spurs before they have a chance to start forming. Here are some beneficial treatment options:
The stretches and exercises linked above.
Splinting, bracing and taping: A chiropodist can give you a splint or boot cast. This helps the inflamed plantar fascia heal by preventing it from tightening during rest periods. Chiropodists can also use therapeutic tape to hold the plantar fascia in place and reduce excess strain.
Custom orthotics provide cushioning and heel support, thus helping people cope with day-to-day heel pain. Everyday use of custom orthotics can also help refine your biomechanical movement and gait(the way you walk). This sets you up for success and prevents heel spurs from developing again.
A footwear overhaul: replace all ill-fitting footwear with shoes that provide heel support, including orthopaedic shoes. Chiropodists can offer footwear advice, and Feet First Clinic staff can provide shoe fittings.
Superfeet insoles are high-quality over-the-counter insoles that easily fit into your shoes. They can help you manage heel pain and provide other benefits, like long-lasting cushioning.
Do You Need a Foot Clinic? Contact Feet First Toronto!
Plantar fasciitis and heel spurs can be challenging to manage on your own. That's why our trusted chiropodists are available six days a week to give you the treatment and education you deserve. Our Bloor West foot clinic is equipped with knowledgeable staff and the guidance you need to get you feeling as happy and healthy as possible. Also, be sure to consult our product catalogue for more information on what's in store in our one-stop shop!
February 9, 2023
Toe pain can be mysterious. There are numerous causes, and sometimes you can live your life assuming you know why it's there, only to be completely wrong! Case in point: a lesser-known toe condition called capsulitis.
Capsulitis is an overuse injury that mainly targets the second toe and the surrounding area. Today we'll thoroughly dive into the topic by addressing the following:
What is capsulitis?
Symptoms of capsulitis
Causes of capsulitis
Treatment and prevention
Complications
What is Capsulitis?
Capsulitis, also known as frozen toe, hallux rigidus or turf toe, is a foot condition characterized by joint inflammation in the area where the base of the toe meets the ball of the foot. The specific area affected is called a "capsule" and is technically a dense ligament structure found at the base of the joint. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, capsulitis in the feet usually targets the second toe. However, it can sometimes affect the big toe and the third and fourth toes. Another technical term for capsulitis in the toe is metatarsophalangeal synovitis (MTP joint pain).
Healthline also notes that capsulitis is often confused with Morton's Neuroma since pain radiates toward the ball of the foot in both conditions. However, Morton's Neuroma results from compressed nerves and capsulitis from inflammation. A chiropodist can help you tell the difference between the two conditions.
Symptoms of Capsulitis
Capsulitis often worsens as time progresses. This means that symptoms can vary depending on the stages of development. It's important to be in tune with your foot health and seek help if you notice the following:
Pain in the ball of the foot.
A persistent feeling that something is "bunched up" in your shoe or the feeling that you're walking on a pebble or marble.
Swelling in the base of the affected toe.
Discomfort while wearing shoes.
Pain that worsens when you're barefoot.
Crossover toe: as degradation of the ligament progresses, the joint in the second toe can fail to stabilize (stay in the right position). This can cause your second toe to move towards the big toe and lay on top of it.
What are Some Causes of Capsulitis?
Capsulitis is technically an overuse injury that targets the ball of the foot. And as with many foot conditions, one issue can often be a risk factor in developing another.
The following may lead to capsulitis development:
There is a connection between severe bunions and capsulitis. Other prominent foot deformities like hammertoes can also be a risk factor. Both conditions can lead to too much pressure on the ball of the foot and subsequent inflammation.
Abnormal foot mechanics can put you at risk. It's important to note that this is not the same as a severe foot deformity. It simply means any mild structural factors that lead to excessive weight-bearing pressure in the ball of the foot underneath the toe.
If your second toe is longer than your big toe, you may experience capsulitis.
An unstable foot arch, like high arches and flat feet, can contribute to capsulitis.
Excessive bending of the toes. This can happen if you wear poorly designed shoes or high heels.
Capsulitis Treatment and Prevention
It's relatively easy to tackle early-stage toe capsulitis. You can purchase many items from a pharmacy, general store or foot clinic that can relieve the pain. A chiropodist can also use their unique expertise to ensure the condition improves.
Here are some effective treatment methods:
Ice or heat packs. Compression can help reduce swelling, and applying heat or ice (while resting with your foot elevated) can help with pain management.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen.
Supportive footwear with proper arch support and strong soles. Rocker bottom-sole shoes can be especially helpful as they offset pressure away from the ball of your foot.
Custom orthotics can lessen excessive pressure on the weight-bearing foot areas.
Toe taping can align the second toe and prevent crossover toe.
Complications
Unfortunately, if crossover toe is present, it usually means that the second toe will never revert to its natural position without intervention. If this is the case, you may need surgery from a foot and ankle surgeon.