Flat feet and plantar fasciitis are closely linked, with flat feet often contributing to the development of plantar fasciitis. Both conditions can also lead to foot pain and mobility issues, and can worsen over time if not properly addressed. Today’s article will answer:
- What are flat feet?
- What is plantar fasciitis?
- What is the connection between flat feet and plantar fasciitis?
- How can I treat flat feet and plantar fasciitis?
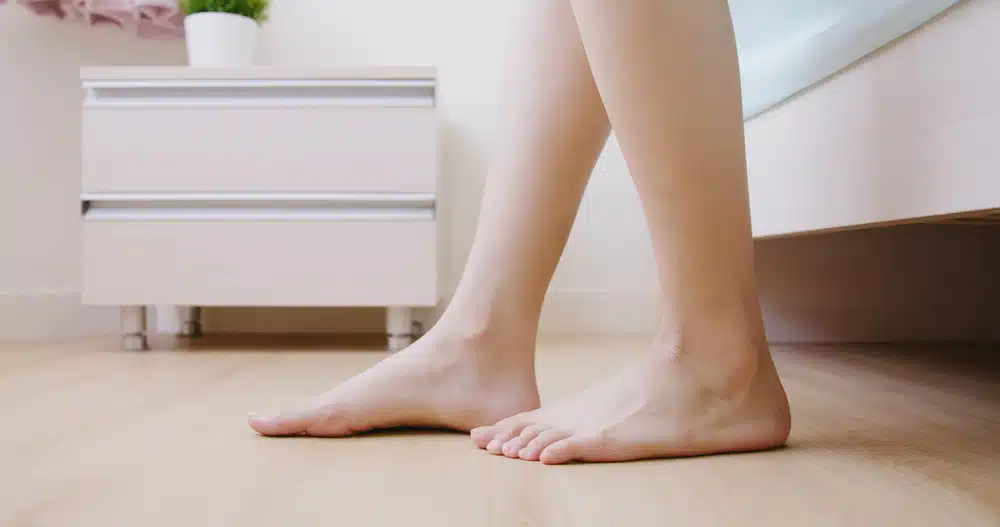

What are Flat Feet?
Flat feet, scientifically called pes planus, is a condition where you have a very minimal or non-existent foot arch. It is one of three arch types, the others being a normal arch and a high arch. If you have flat feet, your entire sole is in constant contact with the ground when you aren’t wearing shoes.
Most children naturally have flat feet but grow out of it as they get older. If you don’t grow out of it by adulthood, it is called congenital flat feet.
Some adults may also have normal arches that collapse. This condition, which may affect one or both feet, is sometimes called adult-acquired flatfoot or fallen arches (both commonly referred to as simply flat feet or flatfoot), and may be asymptomatic. However, it often results in discomfort, foot pain and biomechanical issues.
Many people may not realize they have an abnormal arch or how it affects the rest of our body. That’s why it’s important to talk to a podiatrist or chiropodist whenever you experience foot pain. They can determine whether your pain is directly linked to your foot type and arch structure before offering the appropriate treatment.
Causes of Adult-Acquired Flat Feet
Common causes of adult-acquired flat feet are:
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD): PTTD is a medical condition involving damage, weakening, or inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon, which supports the arch of the foot. It is one of the leading causes of fallen arches in adults. Left untreated, PTTD can progress to foot arch pain and flat feet, often in only one foot.
- Aging: As you age, the ligaments, tendons, and muscles in your feet lose elasticity and strength. This natural wear and tear can result in the gradual flattening of the arch.
- Obesity: Extra body weight increases pressure on the feet, especially the arches. This additional load can accelerate the breakdown of the foot’s structures, leading to flat feet.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This condition can affect the joints and soft tissue in the foot, weakening the ligaments and structures that support the arch, and leading to its collapse.
- Injury or Trauma: Injuries to the foot or ankle, such as fractures or sprains, can damage the tendons or ligaments that support the arch. This can disrupt the foot’s normal structure and collapse its arch.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can relax the ligaments in the body, including those in the feet. This can cause the arch to flatten, often temporarily, but it may persist in some women after childbirth.
Overpronation
Flat feet are a structural issue. Think of a normal arch as an important component of a home; when it is lacking, your foot’s utility and functionality will be affected, as well as your mobility. This means you may subconsciously start walking in an abnormal way to make up for the absent arch and accommodate foot pain, which causes even more damage over time. For people with flat feet, this movement is called overpronation.
When you overpronate, the foot rolls too far inward during walking or running, and becomes a consistent feature of your gait (your walking pattern). This leads to uneven pressure distribution which can cause pain and contribute to injuries in the feet, ankles, knees, back and hips.
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
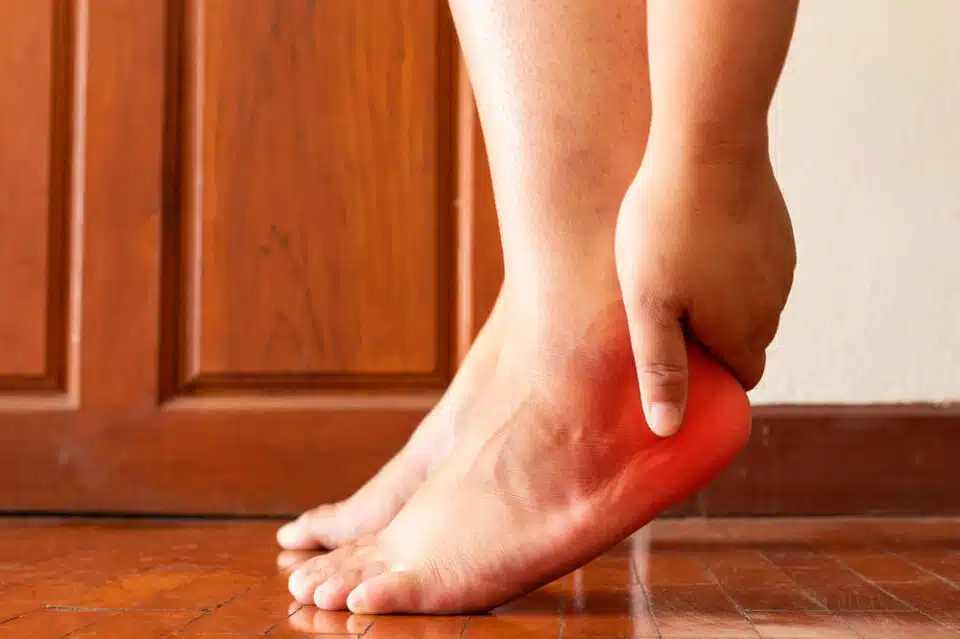
Plantar fasciitis is technically an overuse injury. It targets the plantar fascia, which is a long, fibrous ligament (or band of tissue) that runs along the toes to the heel, connecting the bones of the foot.
The plantar fascia also operates as a dynamic support mechanism for the foot’s arch, distributing forces evenly during movement. When overused, it may lose elasticity and develop microtears, typically near its attachment point at the heel. This then leads to inflammation, your body’s natural response to injury.
If untreated, plantar fasciitis can lead to impactful gait changes, prolonged foot pain, and secondary issues in the knees, hips, or lower back.
Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms
- Heel Pain (especially in the morning): This is a hallmark symptom. During rest, the plantar fascia tightens. When taking your first steps after waking, the tissue is suddenly stretched, leading to sharp pain. As the fascia warms up, the pain often decreases.
- Pain after prolonged standing or activity: Standing for long periods or engaging in weight-bearing activities places repetitive strain on the plantar fascia. This results in pain that often intensifies after the activity ends.
- Tenderness or stiffness in the heel area: The attachment point of the plantar fascia to the calcaneus (heel bone) is a common site for inflammation and microtears, leading to localized stiffness and tenderness, especially after inactivity.
- Swelling in the heel or arch: Inflammation from repeated stress might cause fluid accumulation in the affected area, causing visible or palpable swelling as the body tries to repair itself.
- Worsening pain with barefoot walking or unsupportive shoes: Walking barefoot or wearing shoes without adequate arch support increases strain on the plantar fascia.
- Foot arch pain: Inflammation of the plantar fascia can irritate nearby areas, causing burning or aching sensations along the length of the fascia in the arch of the foot.
The Connection Between Flat Feet and Plantar Fasciitis
Studies suggest that you are more likely to develop plantar fasciitis if you have flat feet versus a normal arch, making flat feet a top risk factor for plantar fasciitis.
This is mainly because the foot and gait mechanics associated with flat feet put excess strain and pressure on the plantar fascia. In a normal foot, the arch acts as a natural shock absorber, distributing weight and reducing stress on the plantar fascia. However, since people with flat feet have a low or entirely absent arch, it disrupts this natural shock absorption from occurring.
Overpronation also strains the plantar fascia, causing microtears and inflammation over time. Additionally, the misalignment caused by flat feet can lead to uneven weight distribution, increasing stress on the plantar fascia and exacerbating the condition.
These factors can also place additional strain on surrounding structures, such as the Achilles tendon, which will worsen the overall tension in the plantar fascia.
Additional Plantar Fasciitis Causes and Risk Factors
Aside from people with flat feet, plantar fasciitis is also common in:
- Middle-aged Adults: Particularly those aged 40 to 60, as natural wear and tear over time can weaken the plantar fascia.
- Athletes: Runners, dancers, and those involved in high-impact sports are at increased risk due to repetitive stress on the plantar fascia.
- People with high arches: Having a high arch, the polar opposite of a flat foot, can also cause plantar fasciitis due to increased strain on the plantar fascia and excessive supination (when the foot rolls excessively outward during walking and running).
- People struggling with obesity: Carrying extra weight increases pressure on the plantar fascia, especially during standing or walking.
- Workers who stand for long hours: Healthcare workers, factory employees, restaurant staff, construction workers and more are at a higher risk due to the repeated strain from standing.
Plantar Fasciitis and Flat Feet: Treatment
If you’re looking for flat feet and plantar fasciitis pain relief, visiting a foot specialist, like a podiatrist or a chiropodist, is your best bet. These experts can provide education, treatment services, and “homework” ideas you can incorporate in your daily routine. Keep reading to learn ways you can manage both issues!
Exercises and Stretches
Performing light, simple and effective routines can help strengthen the plantar fascia and manage heel and foot arch pain. Here are some you can try:
Seated toe pulls: Sit with one foot crossed over the opposite knee and use your hands to gently pull your toes towards you for 30 seconds. Repeat with the other foot.
Towel pickups: Stand with your feet flat on the floor and a towel placed in front of you. Use your toes to scrunch the towel towards you, then relax. Repeat for 30 seconds, then switch feet.
Calf raises: Stand on a step, rise onto your toes, then slowly lower your heel back down. Repeat for 8-10 reps, completing 3 sets.
Read a more detailed article on the best exercises for plantar fasciitis.
Proper Footwear
Wearing the right footwear is essential for managing both flat feet and plantar fasciitis. The key features to look for include:
Arch support: Arch support is the cornerstone of plantar fasciitis treatment. This will keep the plantar fascia properly supported and reduce strain. Arch support also provides stability and helps prevent the overpronation (excessive inward rolling of the foot) that can strain the plantar fascia.
Cushioning: Helps absorb shock, reducing the impact on the heel and alleviating discomfort.
Firm heel counter: Supports the back of the foot, preventing excessive movement and ensuring stability when walking or standing.
Comfortable fit: Ensures the shoe isn’t too tight or too loose. You want to ensure shoes also provide ample space for the toes to prevent overcrowding. This reduces pressure points, allows for proper alignment (which is crucial for people with flat feet) and offers overall comfort.
Midfoot support: Offers additional stability to prevent the arch from collapsing further, keeping the foot properly aligned and supporting a natural gait.
Rounded sole front: A rounded toe or sole at the front of the shoe (like a rocker sole) encourages a smoother toe-off during walking. It can also promote a more natural, efficient gait by allowing the foot to roll more fluidly from heel to toe.
Stability and motion control shoes: These are designed to address the unique needs of people with fallen arches and excessive overpronation to keep your feet in a neutral position during movement. They provide enhanced arch support while controlling foot and ankle motion with firmer midsoles and medial posts (a denser material on the inner side of the shoe), all the while reducing strain on the plantar fascia.
If these features seem overwhelming and you’re having trouble finding the right shoes, our one-stop-shop Toronto foot clinic offers complimentary shoe fittings.
Custom Orthotics
Foot clinics can provide custom orthotics. These are tailored to your foot’s personalized shape, are designed specifically for you and can be worn with many shoe types. For people with flat feet, they provide arch support and reduce excessive pronation. This can help alleviate the stress placed on the plantar fascia, reducing the risk of developing plantar fasciitis and helping alleviate the symptoms of the condition itself.
Shockwave Therapy
This is a non-invasive treatment for plantar fasciitis, and many other conditions as well! It takes minimal time and usually causes relatively little (if any) discomfort. Shockwave therapy works by transmitting low-intensity acoustic waves to the plantar fascia, which promotes healing. The process works by stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms, encouraging the repair of damaged connective tissue and the regeneration of cells in the affected area. Many studies find shockwave therapy to be an innovative, safe and effective treatment for plantar fasciitis.
More Treatment Options for Plantar Fasciitis and Flat Feet:
- RICE method: Rest your foot, wrapped cold compression, and elevate the foot for 5 minutes then remove and wait 5 minutes for it to warm up then walk. This is a tried-and-true plantar fasciitis (and other injuries) treatment you can do from home!
- Joint immobilization: Temporarily restrict movement to allow the inflamed plantar fascia to heal. This can be done with taping, bracing and splinting, or with a boot cast.
- Heel cushioning. Reducing the pressure upon the heel from heel cushions
- Foot Assessment with Video Gait Analysis: Involves recording and analyzing your walking or running pattern to identify abnormal foot mechanics, like overpronation.
- Rolling a tennis ball or frozen water bottle under the foot: Another easy, soothing treatment method you can try at home.